

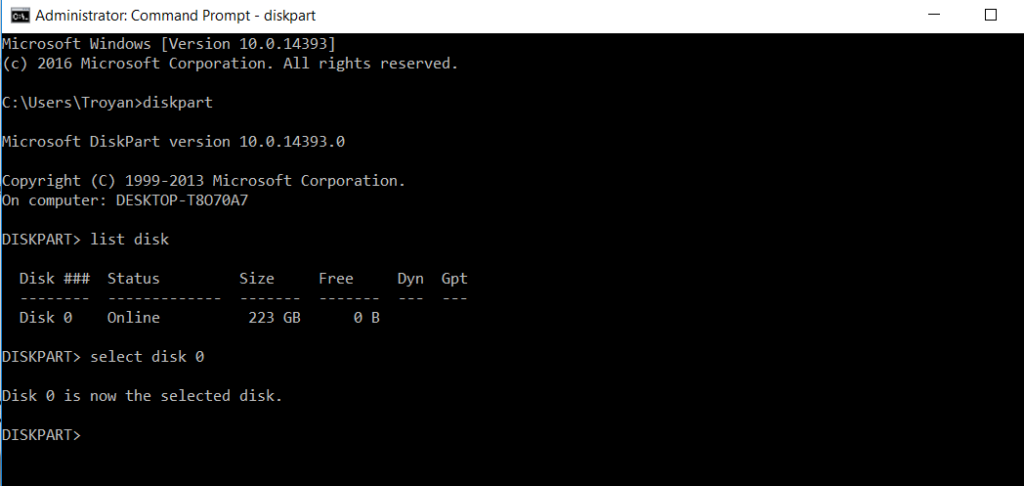
Now let's dive into partitioning and formatting disks on a Linux system. #How to Partition and Format Disk Drives on Linux This logical separation can be useful for a variety of scenarios, including limiting the growth of a filesystem and installing multiple operating systems on a single drive. Creating a partition on a drive logically separates it from other partitions. Common examples of storage devices include hard disk drives (HDDs), solid-state drives (SSDs), USB flash drives, and SD cards. Partitioning is the process of creating logical boundaries on a storage device. Many *nix and Windows operating systems support FAT32. It supports a 4GB max file size and a 2TB max volume size. FAT32 - Is an older filesystem, but you may still see it used in the wild.
LINUX CLEAN DISK COMMAND FULL
The Linux kernel added full support for NTFS in version 5.15. It supports 8PB max volume and file sizes. NTFS - NTFS is a popular filesystem developed by Microsoft.It is not supported on Windows by default. It supports file sizes up to 16TB and volumes up to 1EB.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
